Abstract
We have created an alarm system for the Catalan Surveillance Network of
SARS-CoV-2 in Sewage (SARSAIGUA).
It is based on Principal Component Analysis (PCA).
Two types of alarms are triggered: (1) when the measured concentration of
SARS-CoV-2 is out of normality among all wastewater treatment plants, and (2)
when
one single plant decorrelates from the general trend (useful for early
warning).
The alarms are based on threshold trespassing of two well-known methods:
Hotelling's T2 and Square Prediction Error (SPE or Q).
A web-based interface has been implemented to facilitate the usage and
visualization of the results.
Keywords: Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Fault Detection, Alarm System, SARS-CoV-2, Catalonia, Wastewater Based Surveillance.
Graphical Abstract

Summary
Surveillance networks of SARS-CoV-2 in sewage have been launched in many world countries. Each network selects multiple wastewater treatment plants, taking into account population, spatial coverage, and other technical and/or economic constraints. Once a network is launched, the data generated needs to be transformed into useful information to support decision making.
Analysing each WWTP separately makes it difficult to reach conclusions, hence statistical methods are needed to analyse at once all WWTP data generated from the network.
Catalonia is a region with more than 7.7 million inhabitants in
north-eastern Spain. The Catalan Water Agency (ACA) and the Public Health
Agency of Catalonia (ASPCAT) promoted and funded the deployment of the
Catalan Surveillance Network of SARS-CoV-2 (SARSAIGUA,
https://sarsaigua.icra.cat/)
(
Herein we've applied Principal Component Analysis (PCA, a statistical process control technique) to the time series generated by all WWTPs which are part of SARSAIGUA. This facilitates the identification of single WWTP deviations from the normal behaviour (early warning) and global WWTP deviations from the normal behaviour (generalized outbreak).
Input data used for this study is retrieved from our own API (created ad-hoc). It is available at https://apicovid.icradev.cat/n1. When accessed, the API reads our SQL database (where the labs submit the PCR results every week) and outputs the data in CSV format. The data includes information about the concentration of N1 gene copies at each WWTP and influent flows (in m3/day).
SARSAIGUA covers different plant sizes: from 1,698 to 1,484,787 inhabitants, and from 363 to 334,712 m3/day of average influent flows. In addition, the plants cover zones with different degrees of industrialization as well as with a different touristic pressure.
Manual data quality control on the lab results is executed weekly. This manual quality control involves evaluating: i) RT-qPCR standard curve parameters; ii) recovery values from process control and iii) correlation between RT-qPCR target genes. Whenever large deviations from previous accumulated data in parameters like recovery percentage of a process control are identified, the labs are requested to repeat the sample.
For the analysis, 51 WWTPs (see
| WWTP code | Population (inhabitants) | Average inflow (m3/day) | Sampling frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBSS | 1,484,787 | 334,712 | weekly |
| DPDL | 1,154,006 | 204,328 | weekly |
| DMIR | 241,142 | 49,968 | weekly |
| DTRS | 227,825 | 39,389 | weekly |
| DGVC | 220,302 | 40,082 | weekly |
| DSFL | 206,708 | 48,307 | weekly |
| DMAT | 185,114 | 23,465 | weekly |
| DGIR | 146,609 | 41,619 | weekly |
| DLLE | 145,211 | 51,106 | weekly |
| DSRS | 135,228 | 22,943 | weekly |
| DLLL | 133,252 | 34,485 | biweekly |
| DTAR | 132,381 | 25,266 | weekly |
| DRUS | 108,581 | 15,655 | weekly |
| DRUB | 97,940 | 21,904 | weekly |
| DGRA | 97,393 | 21,138 | weekly |
| DMAS | 92,243 | 20,646 | weekly |
| DVLG | 80,910 | 15,554 | weekly |
| DMDV | 76,690 | 30,441 | biweekly |
| DIGU | 65,757 | 17,459 | weekly |
| DABR | 65,160 | 16,187 | weekly |
| DVDP | 62,122 | 14,006 | weekly |
| DVIC | 55,679 | 22,118 | weekly |
| DPAM | 55,339 | 14,984 | weekly |
| DFIG | 52,048 | 13,319 | weekly |
| DVEN | 49,850 | 11,398 | weekly |
| DVLC | 49,663 | 35,768 | weekly (summer) |
| DOLO | 40,127 | 15,273 | weekly |
| DBLN | 39,028 | 8,673 | biweekly |
| DLDM | 38,373 | 9,768 | biweekly |
| DCPA | 38,008 | 13,921 | biweekly (summer) |
| DTOT | 36,005 | 5,722 | weekly |
| DMRT | 35,801 | 7,731 | weekly |
| DBAY | 27,959 | 10,695 | weekly |
| DMAN | 27,898 | 5,307 | weekly |
| DVAL | 22,410 | 9,304 | biweekly |
| DFON | 22,005 | 22,208 | biweekly |
| DAMP | 20,738 | 3,964 | weekly |
| DRSS | 19,550 | 9,191 | biweekly (summer) |
| DBAL | 17,162 | 7,217 | weekly |
| DTRG | 17,098 | 3,284 | biweekly |
| DBER | 16,494 | 4,616 | weekly |
| DMOF | 15,185 | 3,376 | weekly |
| DPUI | 15,120 | 6,790 | weekly |
| DRIP | 13,695 | 7,696 | weekly |
| DSLL | 12,356 | 2,490 | weekly |
| DSOL | 9,509 | 2,367 | weekly |
| DCER | 9,180 | 1,469 | biweekly |
| DMLN | 8,777 | 1,616 | biweekly |
| DMOB | 7,364 | 1,109 | biweekly |
| DBBL | 6,087 | 1,774 | biweekly |
| DTRP | 5,845 | 2,145 | biweekly |
| DVIE | 4,892 | 6,799 | biweekly |
| DGAN | 3,064 | 525 | biweekly |
| DFAL | 2,834 | 363 | weekly (winter) |
| DPSU | 2,220 | 1,026 | biweekly |
| DSOR | 1,698 | 462 | biweekly |
| total | 5,958,422 | 1,363,128 |
wwtps
WWTPs of the SARSAIGUA surveillance network sorted by amount of
serviced population. Also, average influent flows are displayed.
A second input dataset has been prepared: daily reported clinical cases for all municipalites served by each WWTP, weighted by the percentage of inhabitants connected to each WWTP. This data was extracted from the official API of the Information Systems of the Department of Health and the Catalan Health Service (https://analisi.transparenciacatalunya.cat/resource/jj6z-iyrp.json).
The percentage of each municipality's inhabitants connected to each WWTP was requested directly to WWTPs. This information is available here: https://covidvigilancia.icra.cat/formularis/municipis_assistits.json
An input matrix without gaps is required when running PCA. Linear interpolation has been applied to the biweekly-sampled WWTPs (N1 concentration and flows) and missing values due to incidences in sampling (e.g., missing flow data).
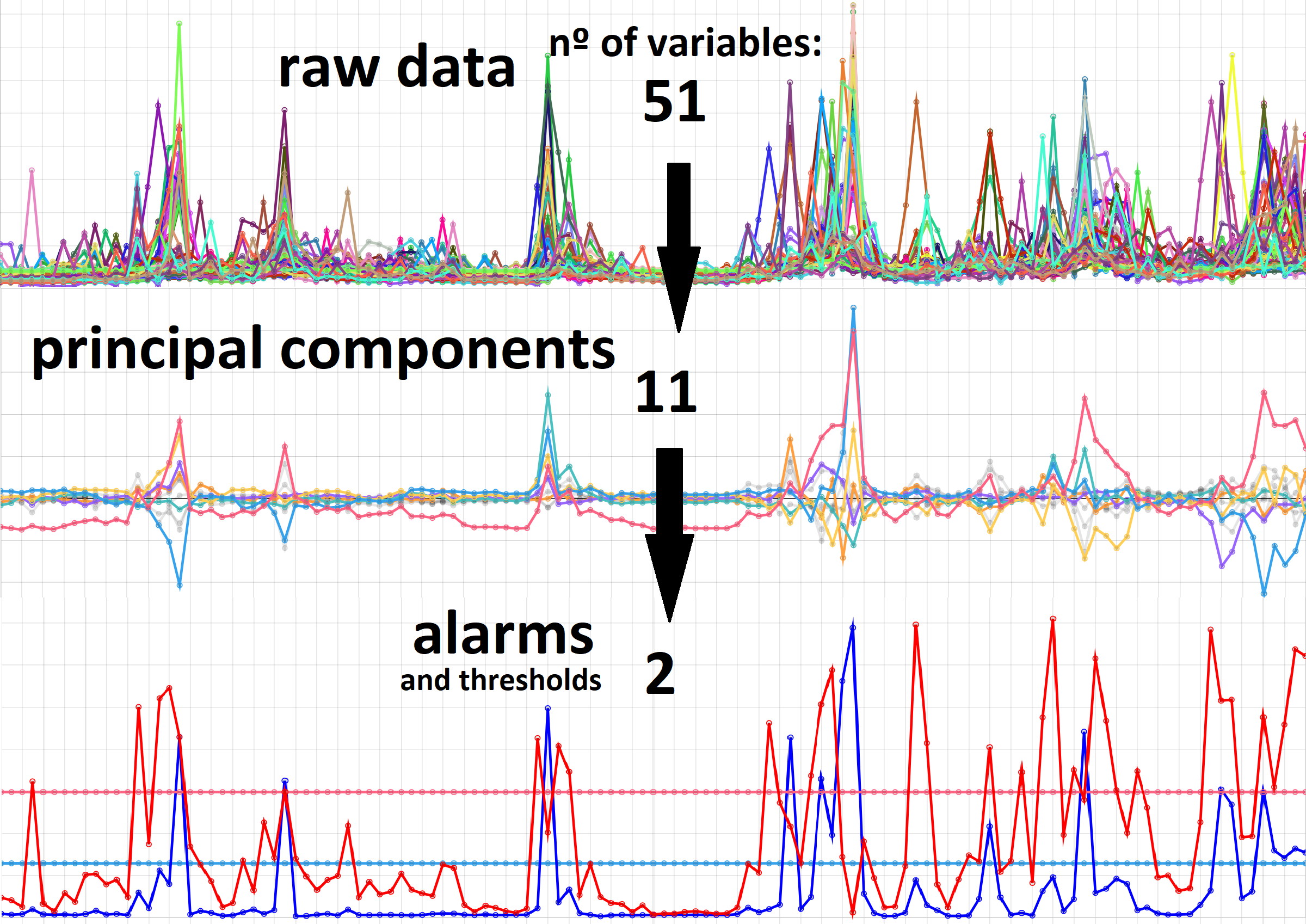
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a multivariant statistical method for exploratory data analysis (unsupervised learning). It can be used to reduce the number of variables in a dataset while retaining as much information as possible.
PCA works by transforming the original variables into a new set of variables, called principal components, which are uncorrelated and ranked in order of importance. These new variables are linear combinations of the original variables: the first principal component is the linear combination that captures the greatest amount of variation in the data. The second principal component is the linear combination that captures the next greatest amount of variation in the data, subject to the constraint that it is orthogonal (i.e., perpendicular) to the first principal component, and so on for the remaining principal components.
PCA can be used for a variety of applications, such as identifying patterns, reducing the dimensionality of data for visualization, and making predictions using machine learning algorithms.
Our goal in this study is to use PCA as a basis for an automated alarm sytem procedure, based on fault detection techniques: (1) the error of reprojection (Squared Prediction Error, SPE or Q), which we've identified as useful for early warning, and (2), the Hotelling's T2, which has the ability to detect shifts in the mean vector of a process; in our case identifies abrupt increases in the general circulation of the virus.
Let X be a complete matrix, containing n observations (rows) and m variables (columns).
| obs nº | WWTP[1] | WWTP[2] | ... | WWTP[m] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X= | 1 | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2 | ... | ... | ... | ... | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | |
| n | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Scaling is performed to each column, to ensure each WWTP is given equal weight in the monitoring process. Involves subtracting each variable by its sample mean (to capture the variation from this mean) and then, divide by its standard deviation. This gives equal importance to all columns (no matter the size) and also removes variabilities caused by different sampling and analytical methods (e.g. analytical differences between labs).
Let S be the covariance matrix of X. Since X is mean centered, it can be calculated as:
S is also the correlation matrix because X is scaled to unit variance. Size of S is mxm.
A Single Value Decomposition (SVD) algorithm is applied to
S:
Let x be any row of X (an observation vector, size
m). Let t be the projection of x into the
matrix V:
Projecting into x into V decouples the observation space into a new set of uncorrelated variables (the elements of t):
The ith column of V is the loading vector pi that transforms an observation x into the "score" t.
To distinguish between the transformed variables and the transformed observations, the transformed variables are called "principal components" and the individual transformed observations are the "scores".
Let a be an integer value between 1 and m.
Let P be the matrix resulting from taking the first a
columns of V, corresponding to the a largest
eigenvalues of S.
P size is mxa.
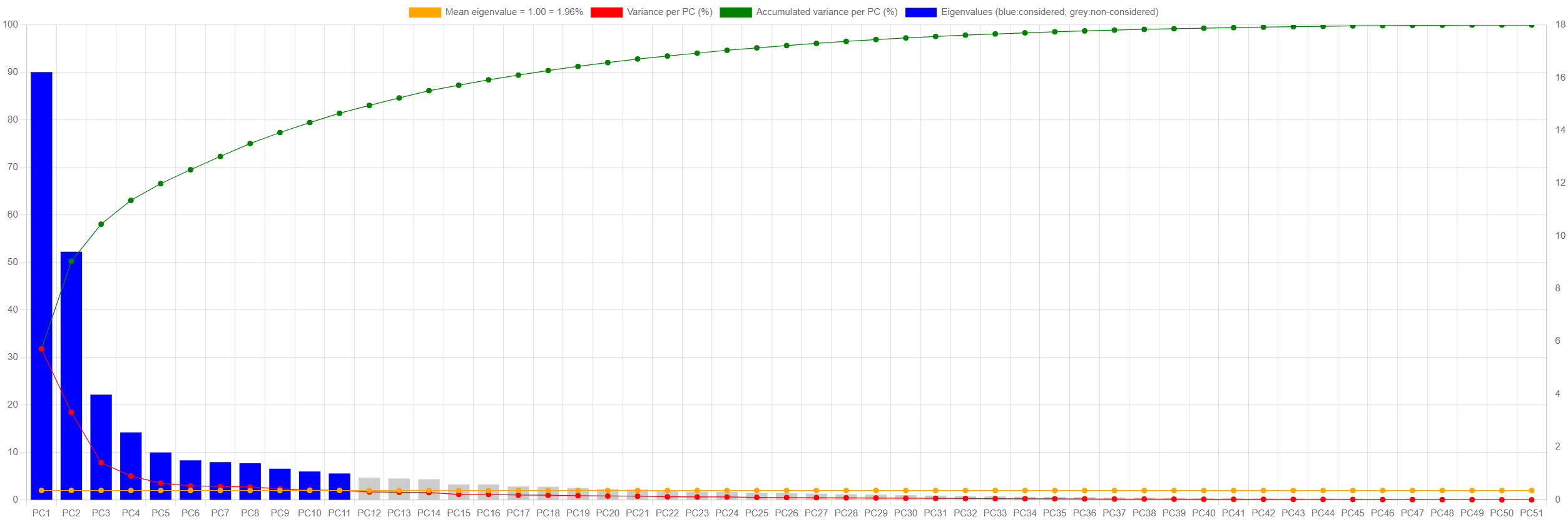
Choosing the value of a is choosing the number of principal components. This choice can be done in multiple ways. In this study we've chosen the number of principal components corresponding to the eigenvalues of S larger than one, which is the same as keeping only the principal components with variance above the average.
Let T be the projection of X into
P, also known as the "scores" matrix.
T size is nxa.
Let Ti be the ith column of T. The following properties can be shown:
Var(T1) ≥
Var(T2) ≥
... ≥
Var(Ta)
.
Let X̂ be the matrix resulting of projecting T back
into the original m-dimensional space.
Size of X̂ is nxm:
Let E be the residual matrix, computed from the difference between
the original X and the back-projection of T.
Size of E is nxm:
Dimensional reduction provided by PCA (from m to a variables) represents nearly the same information in a lower dimension space. This new space can be used for multivariate process monitoring.
The Hotelling's T2 statistic uses the a-dimension space (columns of the matrix T) to detect misbehaviours based on threshold trespassing.
The Q statistic uses the residual matrix (E) to monitor the portion of observation corresponding to the smallest eigenvalues of S (from number a to m).
For every observation in the reduced space (t) we can associate a T2 value, computed as:
The value of T2 can be interpreted as the distance of this observation to the center of the model (mean).
Scores are scaled inversely proportional to the standard deviation along the eigenvectors (columns of P). This allows defining a scalar threshold to characterise the variability in the a-dimensional space.
Given a level of significance (α, chosen as 0.05 in this study), appropriate threshold values for the T2 statistic can be determined. When the mean and variance are estimated from a sample of observations, the threshold is calculated as:
Let r be the residual vector of an observation (x),
computed from the back projection of its scores in the lower
dimensional space.
qnorm(0.95,0,1)).
The T2 chart is useful to detect observations out of normal operation conditions. It is a quality measure of the data according to the model (the first a principal components). It is measured in the direction of the model. If T2 increases, the observation preserves the model structure but with larger values ("far from the mean").
The Q chart detects structural changes in the process. It is a measure of the projection error. It is measured in the error direction (orthogonal to PCs). If Q increases, the correlation structure gathered by the PCA model (the first a components) is not preserved in that observation.
Contribution analysis answers which variable/s in the original space are responsible of the detected fault (threshold trespassing), which we refer to as "alarms" in our study.
For one observation under fault, the contribution of one particular
variable from the original space to the out of control status is:
For one observation vector x under fault, the components of
the residual vector r are directly the contributions to
Q.
All the equations above have been implemented in Javascript. This language choice allows doing all the computation client-side, since it is native in all web browsers (e.g. Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, etc.), regardless of the operating system, and type of device.
The starting point was creating a matrix library from scratch, to perform basic matrix operations (e.g., sum, multiplication, transposition, determinant, inverse...). Then, the SVD algorithm and PCA procedures were implemented. Then the Hotelling T2 and Q statistics, along with the calculation of the contributions.
This matrix library is freely available at https://github.com/icra/matrix-library-js, but at the time of this writing is still not fully documented.
To validate the Javascript implementation, numeric tests were conducted using R (https://www.r-project.org/) since it is a well-known and stablished numeric platform with PCA functions builtin.
The matrix library was then loaded into the web interface, also created ad-hoc, coded in HTML and CSS, and using VueJS (https://vuejs.org/) as the frontend Javascript framework. This approach was selected to facilitate the integration of these developments with the SARSAIGUA platform as a superior layer of analysis, beyond current visualization options.
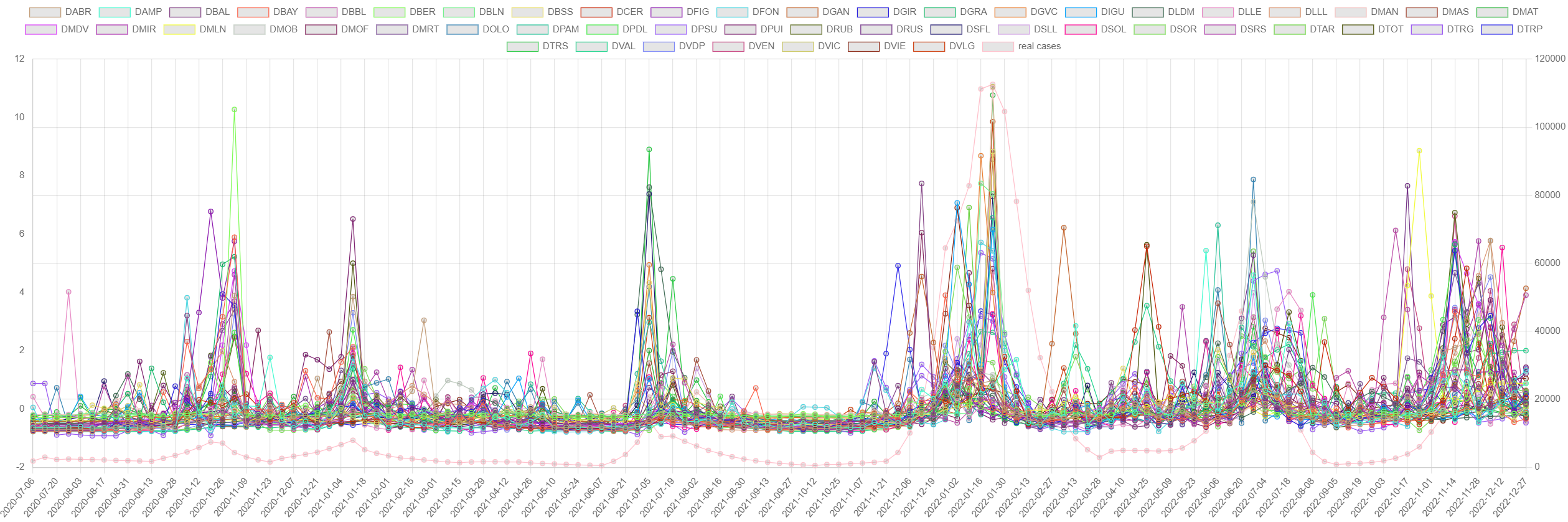
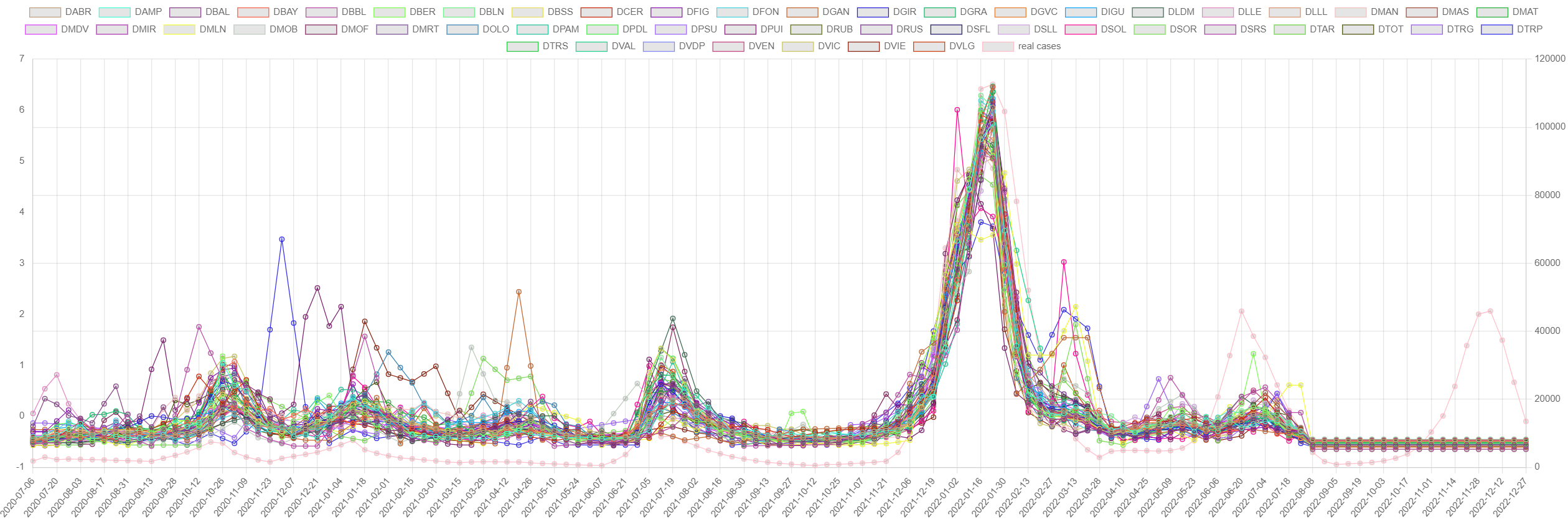
The evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic in Catalonia can be observed in
The most dominant variant of SARS-CoV-2 have been: Delta (until January 2022), Omicron BA.1 (until mid-March 2022), Omicron BA.2 (until mid-June 2022), Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 (until November 2022), and Omicron BQ.1 (current at the time of this writing).
PCA of N1/inhabitant was run with an input matrix X of
125 observations (rows) and 51 WWTPs (columns).
Taking 11 PCs (with associated eigenvalue>1),
82% of the variance was retained
(see
PC1 explains 32% of the variance. This signal is equivalent to the mean of each observation (after scaling it with the standard deviation of the first principal component).
PC2 explains 18% of the variance and distributes WWTPs along
the vertical axis. PC2 captures differences amongst WWTP groups. In
particular, PC2 clusters WWTPs that did not detect 2nd, 3rd and 7th
wave very well, but had a very strong detection of 4th, 5th and 6th
wave, and the other cluster is the opposite (see
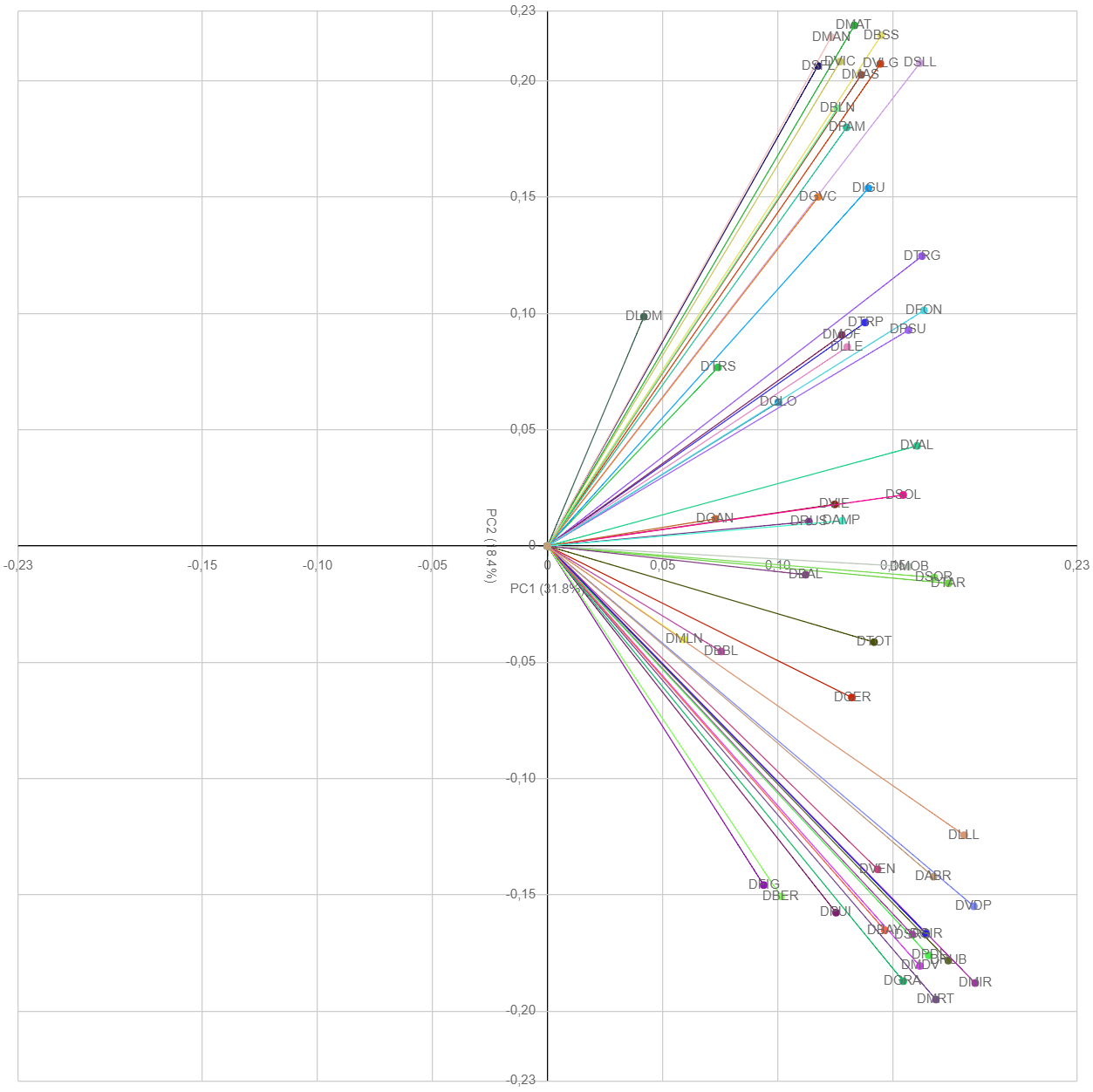
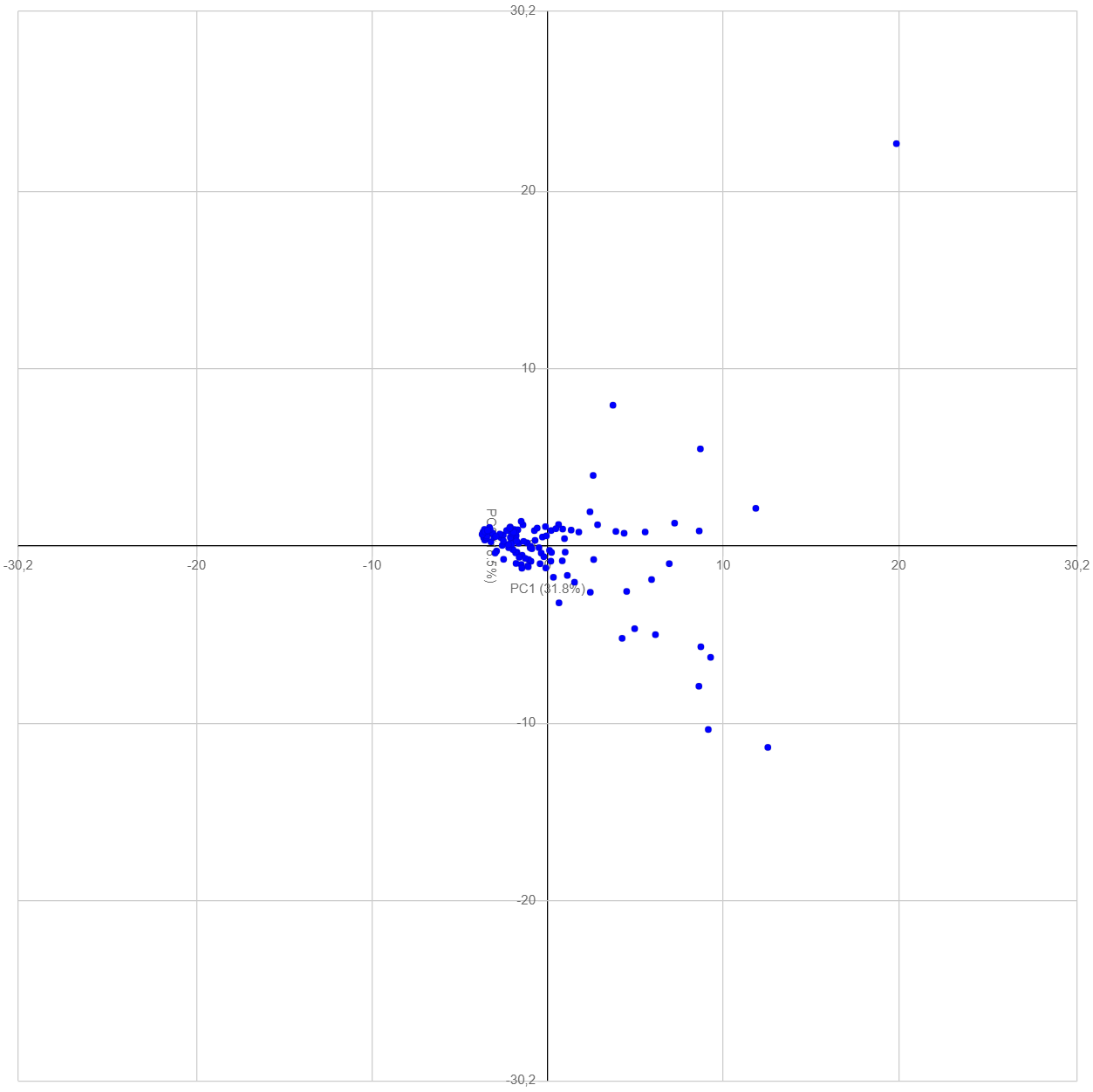
loadings_and_scores
Loadings and Scores (PC1 vs PC2).
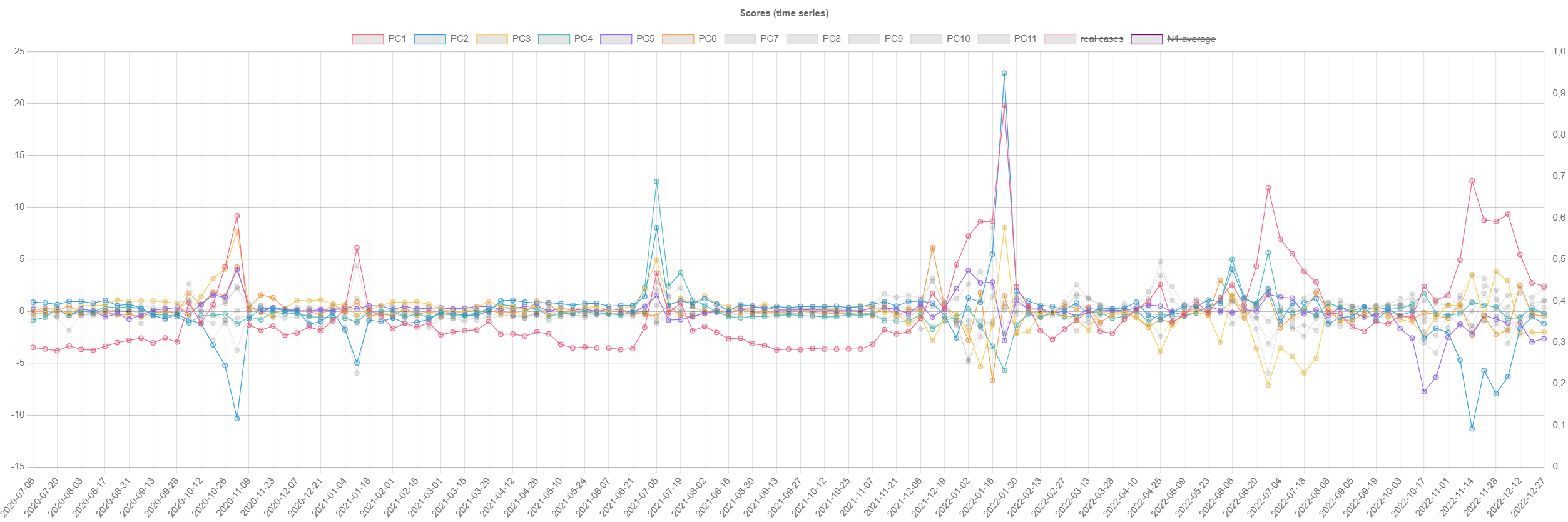
TO DO
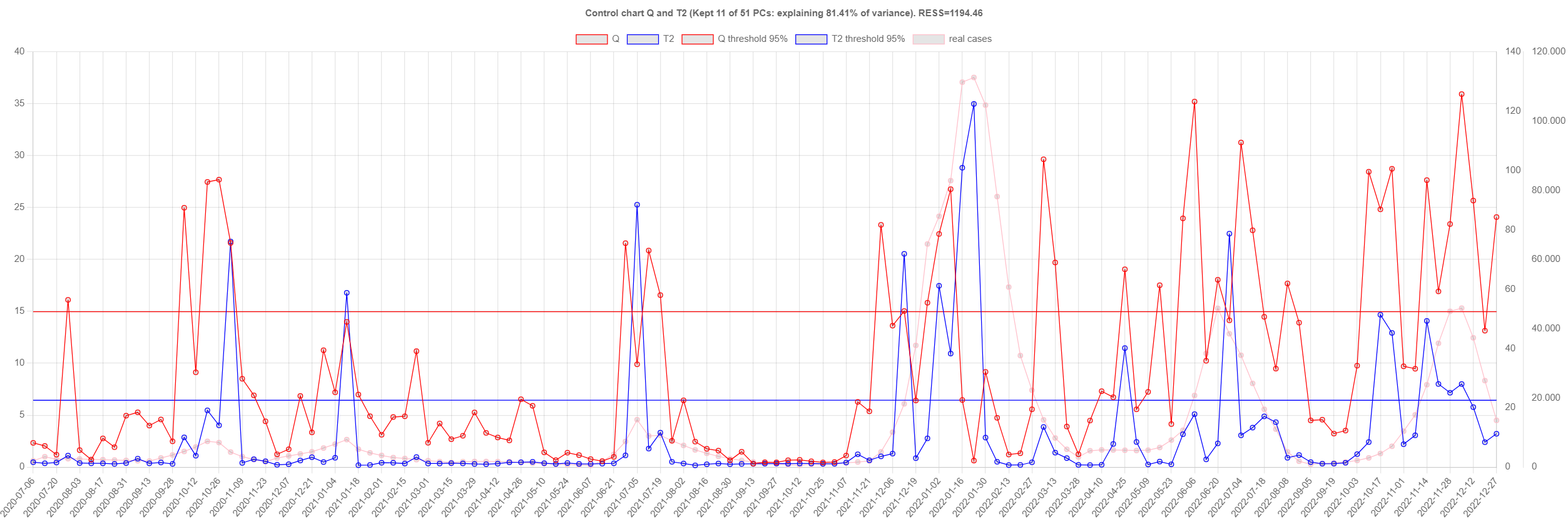
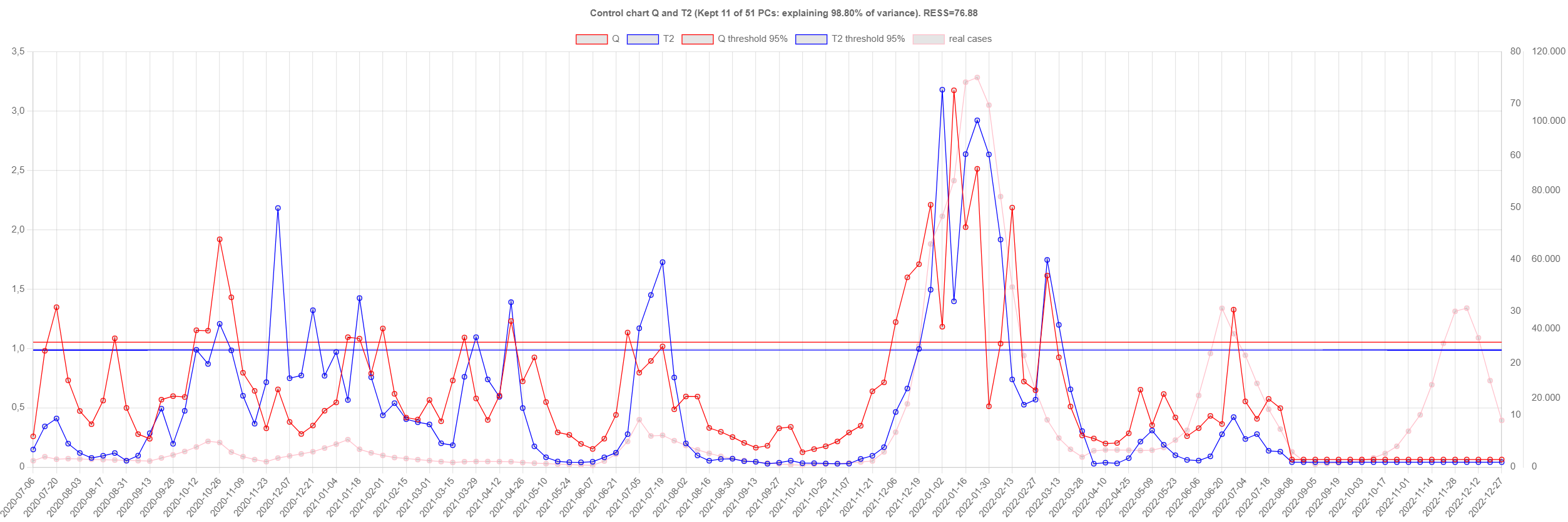
control_charts
Control chart (top: N1/inhabitant, bottom: clinical cases)
with Q and T2 and respective thresholds.
Note that reporting of cases stopped on 2022-08-01.
One might wonder if the same subset of WWTPs is consistently
triggering alarms; the response is not.
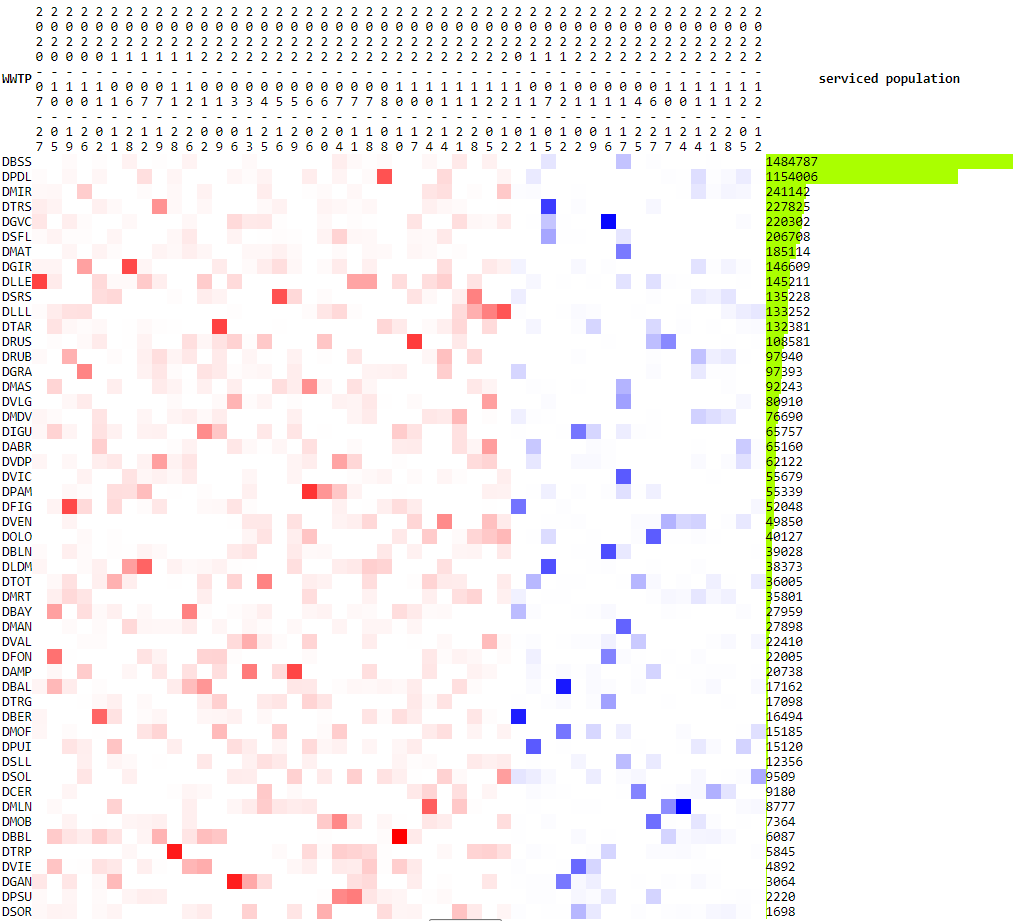
Contributions to alarms by each WWTP, sorted by serviced population
in descending order. Intensity of color is with respect to the
highest contribution among all alarms. Red cells correspond to
alarms for Q. Blue cells correspond to alarms for T2.
The fact that the Q alarms when executed on the clinical reported cases and on wastewater match well, indicates that the ranking in the Q-statistic is more related to the spread of each wave across the territory rather than the sensitivity of the WWTPs. It is also possible that sampling or analytical errors lead to unexpectedly higher or smaller N1 concentrations; such poor data quality values would influence the result of the PCA and trigger false alarms. The developed system allows detecting such abnormal behaviour and tracing back the origin of the alarm to a single WWTP (in that case). Hence, a manual check is needed for each alarm generated, and if generated by a single WWTP or by WWTPs analyzed by a single laboratory, a verification of data quality needs to be conducted before triggering an alarm and communicating to health authorities.
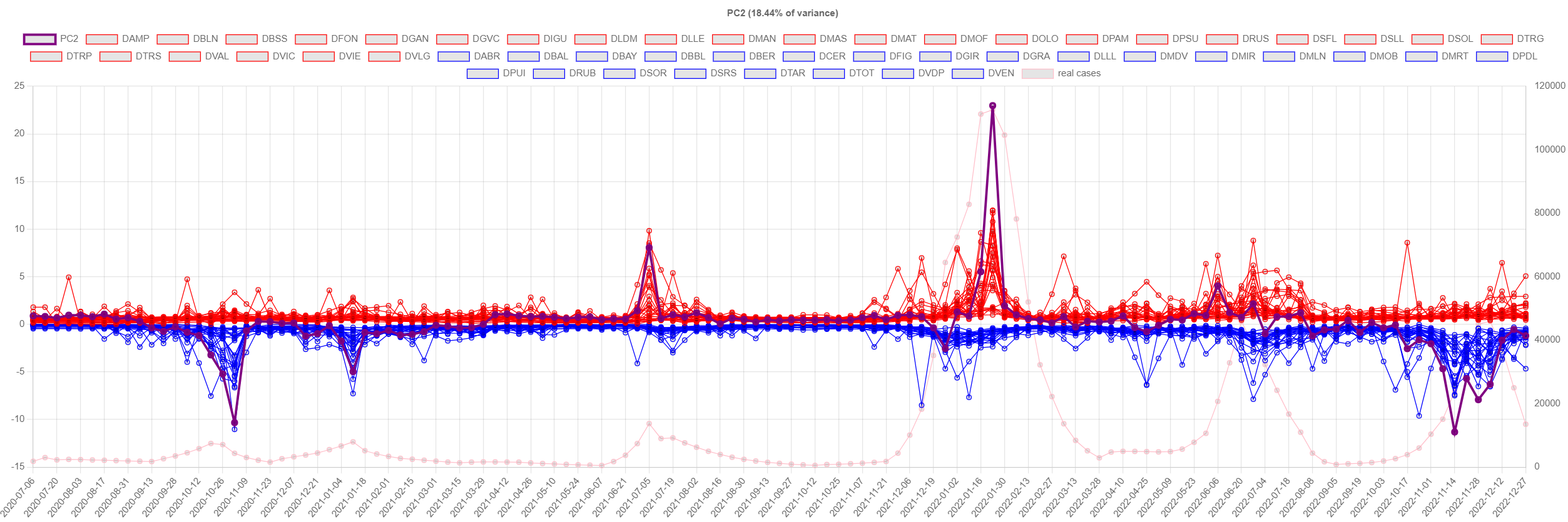
Such a situation happened in one observation, where an unexpected
increase was observed (observation at 2022-08-08 for the WWTP
"DPDL", see
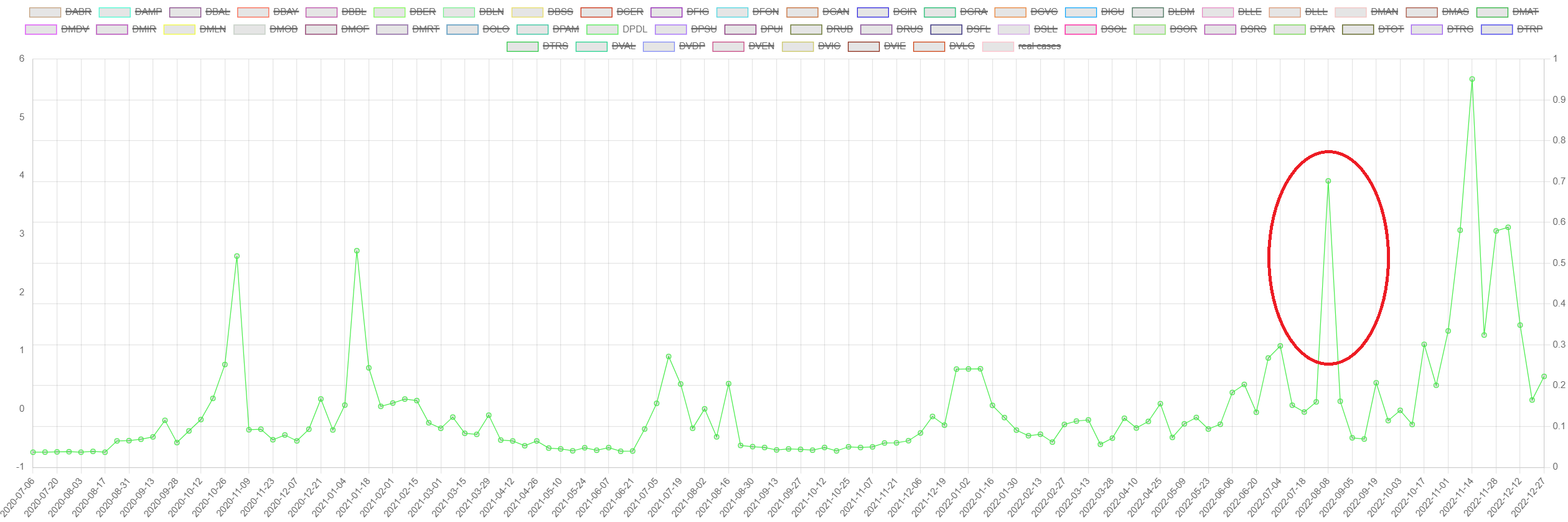
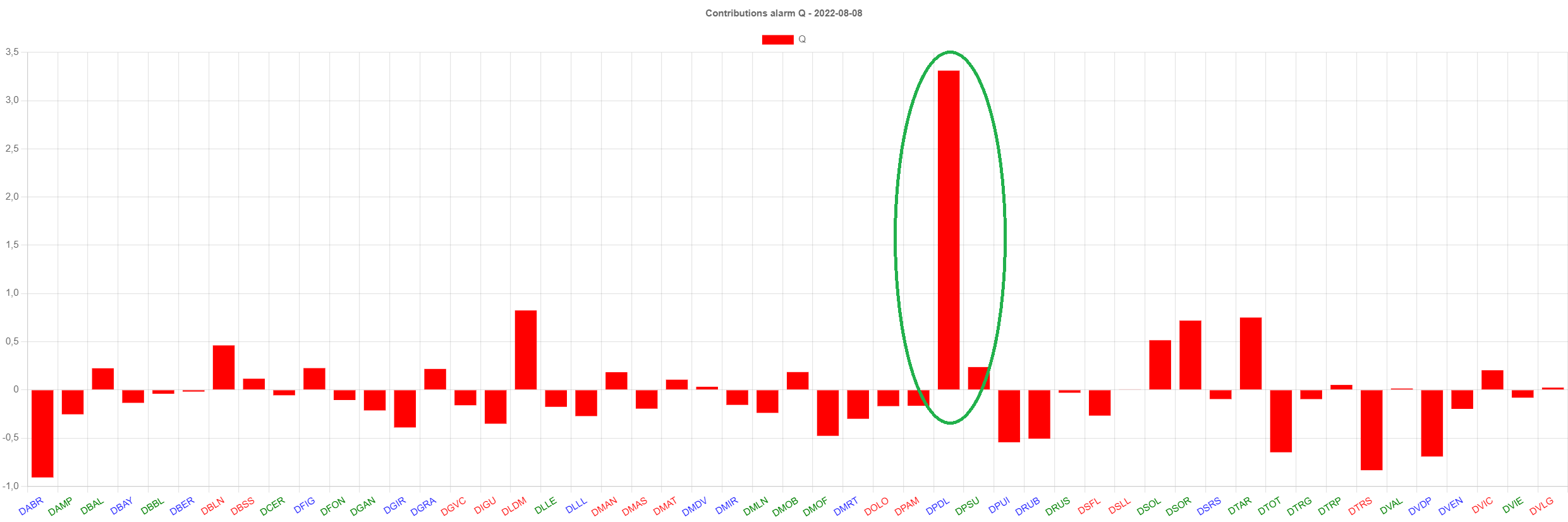
outlier
Values of N1/inhabitant at WWTP "DPDL". It spikes at 2022-08-08. The
alarm system triggers an alarm for Q. Below, the contribution
decomposition by WWTP for the alarm triggered at that day. It
reveals that the largest contribution by far was almost entirely by
that WWTP.
punts clau: